low end tidal co2 after intubation
Reading the Waves When it comes to capnography everyone knows the normal adult respiratory. Confirm ETT placement with end-tidal CO2 detector bilateral breath sounds and chest rise.
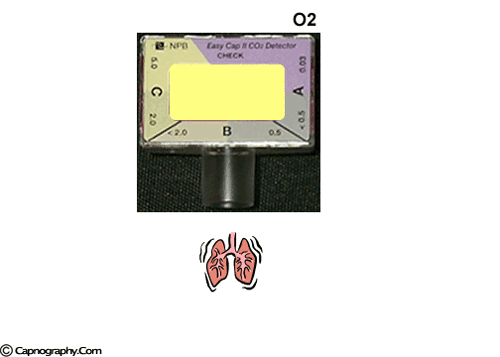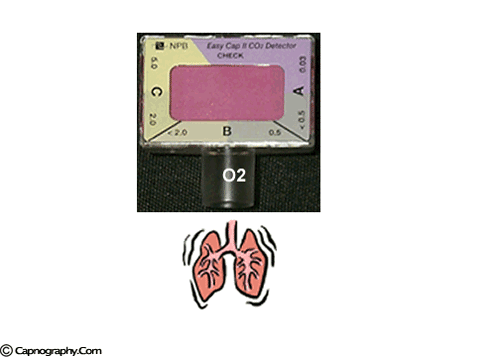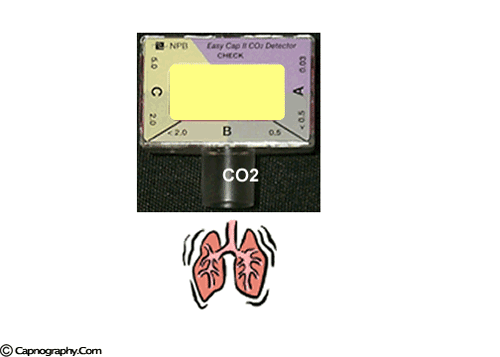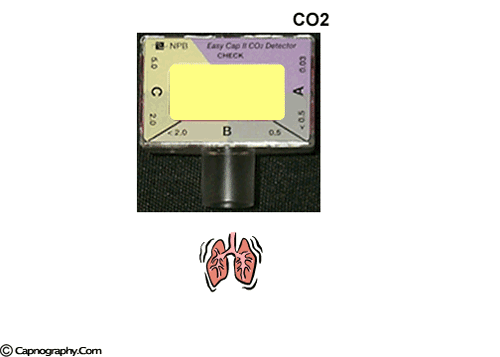
Emergency Intubations Capnography
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis.

. Rapid Sequence Intubation Figure 1-3 End-tidal CO2 detector before application. After intubation if ETCO 2. NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC Vasopressors will decrease ETCO2 they cause high afterload increasing BP and myocardial blood flow but a.
The higher the ETCO2 measured during compressions the better the perfusion being supplied by CPR. High quality chest compressions are achieved when the ETCO2 value is at least 10-20 mmHg. This can be seen in a number of other conditions.
2345 ETCO 2 monitoring is one of the objective standards set in the Intensive. It is pos-sible that carbon dioxide CO 2 remains in the lungs postmortem and is liberated by artificial ven-. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
The effectiveness of out-of-hospital use of continuous end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring on the rate of unrecognized misplaced intubation within a regional emergency medical services. What is end-tidal CO2 etCO2. The depth of the tube for a male patient on average is 21-23 cm at teeth The depth of the tube on average for a female patient is 19-21 at teeth.
The PETCO2_1 and PETCO2_2 measurements were statistically significantly different between the patients who survived and those who died p0014 p0015. ETCO2 is one valuable tool we have to tell us that good quality compressions are being delivered. A maximum Etco220 mm Hg within 5 minutes of the onset of mechanical ventilation in the OR may be useful in decision-making related to the termination of resuscitative efforts during emergent trauma surgery.
The end-tidal CO2 in these people will be unnaturally low. Measurement of a low ETCO2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient would indicate that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
1 Arterial CO2 should be higher than etCO2. The alpha angle is the transition from Phase II to Phase III. However a large-scale study is needed to establish the statistical reliability of this finding before potential adoption.
An ETCO2 below 10 mmHg is associated with poor outcome. End-tidal carbon dioxide cannot be used to rule out severe injury in. Extraordinarily rarely etCO2 can be slightly higher than arterial CO2 in pregnant patients with otherwise normal lungs.
Asplin BR White RD. An end-tidal capnography waveform measures and displays the peak amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation. After intubation if ETCO 2.
Massive pulmonary embolism Contamination of CO 2 detector with gastric contents or acidic drugs including epinephrine administered via the endotracheal tube Severe airway obstruction status asthmaticus. Immediately after intubation as measured by the capnography the initial PETCO2_1 and at post-ventilation 15 min PETCO2_2 and first second arterial blood gas analysis are recorded. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa.
Evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions is accomplished in the following manner. The goal should be to maintain ETCO2 no lower than 10-20 mmHg. This leads to two foundational principles of etCO2.
End-tidal CO2 measurement in the detection of esophageal intubation during cardiac arrest. MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST. A low end-tidal CO 2 in hypothermia In hypothermia the total body CO 2 production is greatly decreased as the metabolic rate is decreased by 6 for every degree below 36.
A purple indicates low levels and probable esophageal intubation. Bhende MS Karasic DG Karasic RB. Reassess tube placement patency and depth in.
The Difference Between Arterial and End Tidal CO2. 3 By the time gas reaches the endotracheal tube the end-tidal CO2 concentration will be lower than the arterial CO2 tension. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis.
Instances associated with false negative end-tidal CO 2 readings after successful endotracheal intubation also include. The gradient between the blood CO 2 PaCO 2 and exhaled CO 2 end-tidal CO 2 or PetCO 2 is usually 5-6 mm Hg. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis.
NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

3 Things To Know About Capnography And Advanced Airways Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Etco2 Tutor By Satish Deopujari Tutor Telemedicine Learning

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
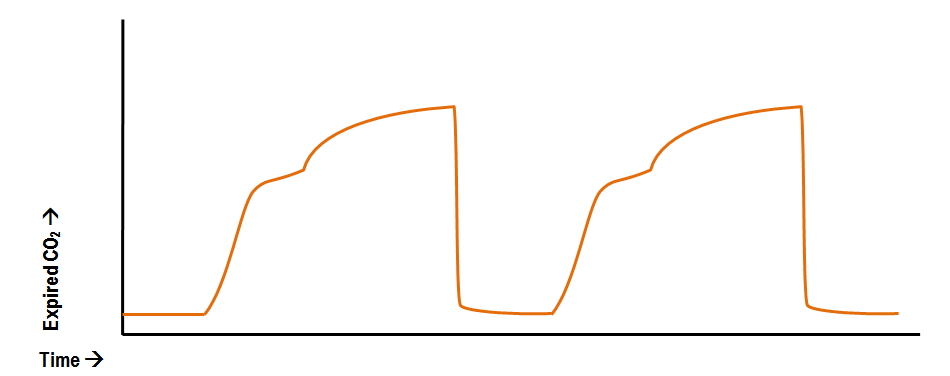
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

Making Paracentesis Better Safer With Pocus Ultrasound School Critical Care Nursing Icu
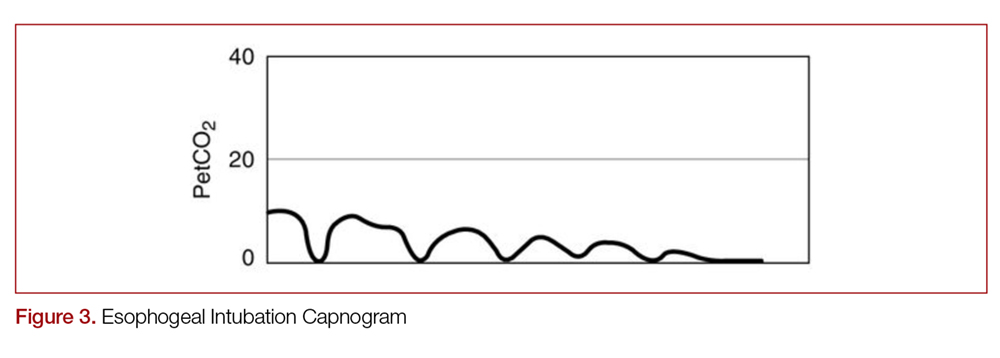
End Tidal Capnography In The Emergency Department Mdedge Emergency Medicine

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Approach To Intubation Infographic

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Effects Of Airway Management And Tidal Volume Feedback Ventilation During Pediatric Resuscitation In Piglets With Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest Scientific Reports

Ventilator Waveform Troubleshooting High Peak Pressures This


